Introduction to Ethereum
Ethereum, a decentralized open-source blockchain system, introduced its own cryptocurrency, Ether, and revolutionized the digital landscape. Founded in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum facilitates not only transactions but also executes decentralized smart contracts, setting it apart from traditional cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
The Genesis of Ethereum
In 2014, Ethereum raised over 31,500 BTC through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO), marking its entry into the crypto world. Unlike Bitcoin’s finite supply, Ethereum boasts an infinite supply, with over 122.7 million ETH in circulation today.
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin
Ethereum stands distinct from Bitcoin, with over 122 million tokens in circulation, over ten times that of Bitcoin. Launched in 2015, Ethereum was conceptualized by Buterin and a team of visionaries, envisioning a platform beyond mere digital currency.
The Ethereum Blockchain: Powering Decentralized Finance
Ethereum’s blockchain, dominating over half of the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) market, serves as the backbone for innovative financial solutions. Its significant market share renders any changes or developments impactful, as seen during the Ethereum Merge of September 2022.
The Ethereum Merge and Proof-of-Stake

Transitioning from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) in September 2022, Ethereum revolutionized its energy consumption dynamics. The move towards PoS, akin to Solana and Cardano, heralded a significant reduction in energy consumption, enhancing sustainability and scalability.
The Ethereum Split and Mining Dynamics
Following the Ethereum Merge, dissenting miners split off, seeking alternative cryptocurrencies to mine. This split not only impacted Ethereum’s ecosystem but also highlighted divergent opinions within the mining community.
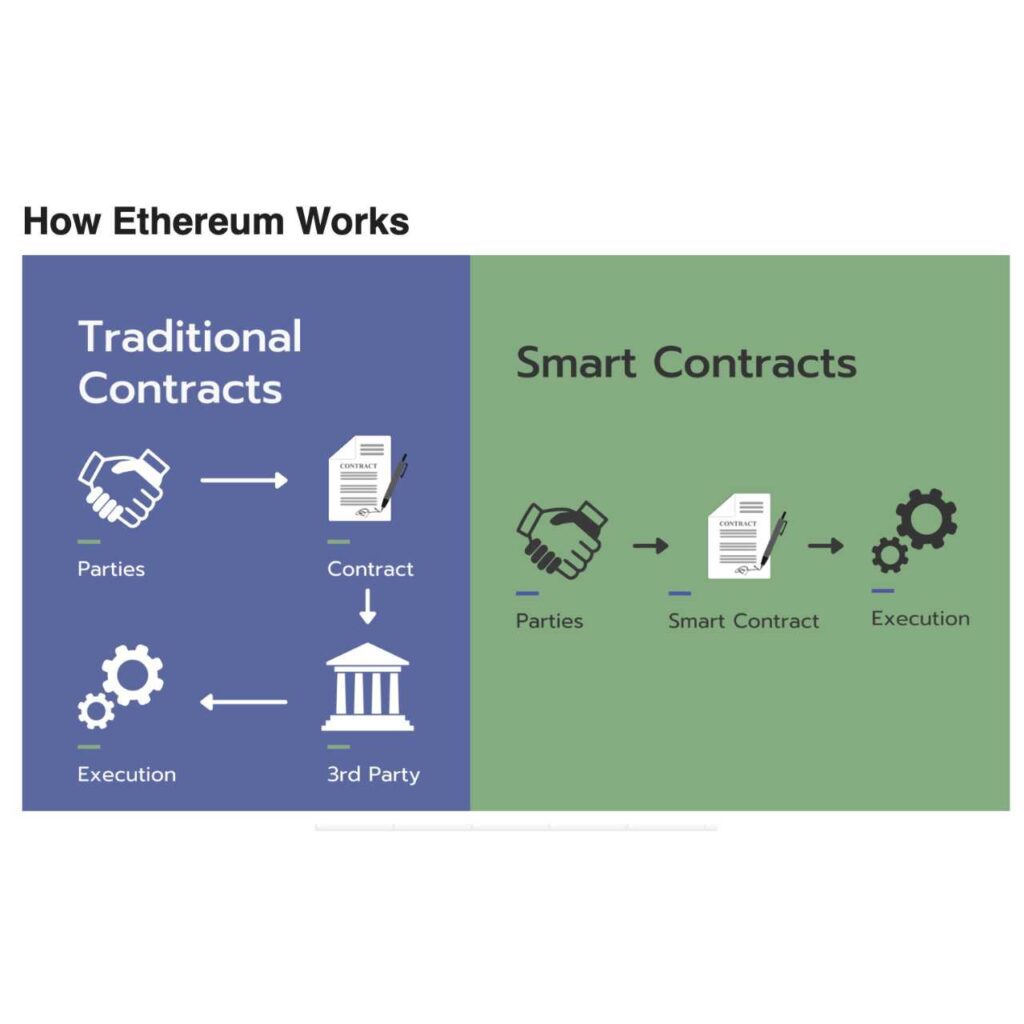
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum operates as a decentralized blockchain platform, enabling smart contracts and applications devoid of third-party intervention. Its versatility extends to serving as a programming language for developers, fostering innovation and decentralization.
Ethereum Use Cases: Decentralized Finance, NFTs, and DAOs
Ethereum’s applications span diverse sectors, from Decentralized Finance (DeFi) to Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). DeFi fosters financial inclusivity, NFTs revolutionize digital ownership, while DAOs embody democratic governance.
OriginStamp’s Integration with Ethereum
OriginStamp harnesses Ethereum’s blockchain to create tamper-proof timestamps, ensuring data integrity and authenticity. These timestamps, essential for proving the existence and integrity of digital assets, showcase Ethereum’s versatility beyond financial applications.
Conclusion
As Ethereum continues its upward trajectory, it emerges as a pivotal player in the digital revolution. With a myriad of applications and a robust infrastructure, Ethereum is poised to redefine not only finance but also governance and digital ownership in the years to come.
















What do you think?
It is nice to know your opinion. Leave a comment.